Despite high adoption rates and a myriad of choices, the complexity of many medical software systems can frustrate even the most technologically literate provider.
Interoperability woes can make it difficult to share and view medical images from disparate systems, especially if providers are using outdated EMR software or don’t have a Picture Archiving and Communication System (PACS). As medicine moves towards a film-less future, providers must have the software tools necessary to share, view, or edit medical images. To accomplish this, many providers are choosing standalone DICOM viewers.
DICOM stands for Digital Imaging and COmmunications in Medicine. It is an international standard file format and network communications protocol developed by the American College of Radiology (ACR) specifically for medical imaging. Most EHR systems support the DICOM standard for viewing and transmitting images. If you can already view DICOM images within your EHR, you likely won’t require a standalone viewer. However, if your system doesn’t support DICOM, you’re having difficulty communicating with a PACS or RIS system, or if you don’t have PACS/RIS access — or even EHR at all — a free DICOM viewer will help you get started viewing images.
The following systems can help you securely view, edit, and share DICOM images. Some offer paid versions intended for commercial applications, which usually include increased functionality — or at least won’t remind you constantly that you’re using a trial version. The software below is listed in no particular order, and represents some of the better systems on the market.
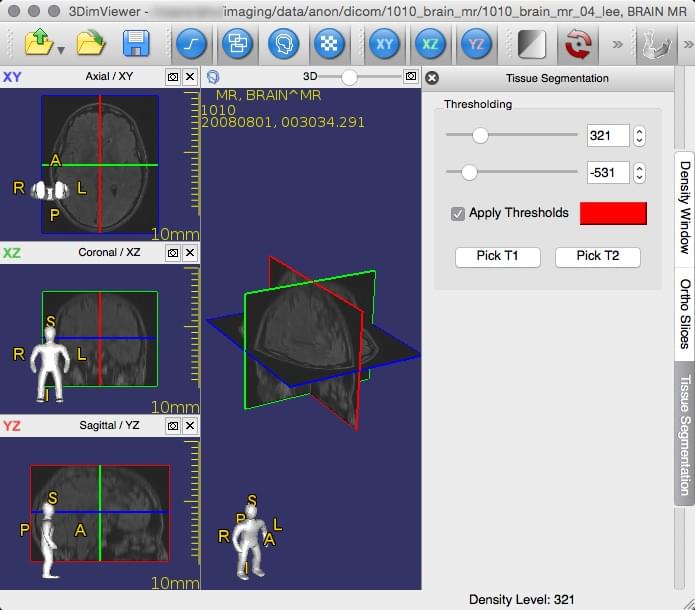
3DimViewer
A smooth, minimalist graphical user interface makes 3DimViewer easy to use and learn. It’s capable of displaying 3D imaging profiles, including multi-planar and orthogonal displays, but it’s specialty is both volume and surface renderings with thresholding-based tissue segmentation. GPU acceleration is necessary for volume rendering, so don’t try to use this on older computers, or even many newer models with integrated graphics chipsets.
Native installers are available for Macintosh, Windows, and Linux-based platforms, making it one of the more flexible systems available. It is also open-source, meaning your developers (if you have them) can use the publicly available C++ code to integrate with it with other programs, or otherwise customize your system. It is a view-only solution — there’s no native editing beyond simple brightness, contrast, etc. Installers for Macintosh and Windows 32 and 64-bit systems are available here — Linux users will have to go to SourceForge.
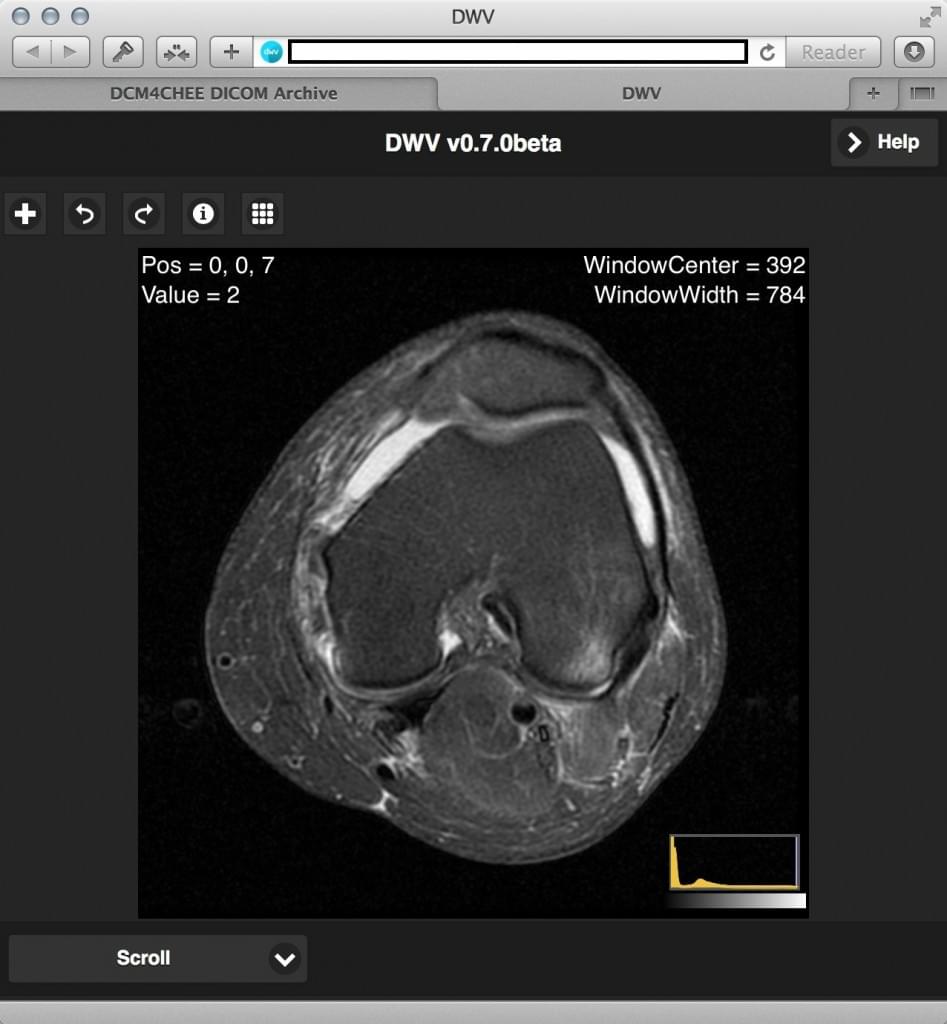
DICOM Web Viewer (DWV)
DWV is a completely browser-based DICOM viewer written in Javascript and HTML5, which means you can use it on almost any device with almost all modern browsers, including laptops, tablets, phones, and even some smart televisions. With some coding, it can be incorporated into any PACS server that supports the Web Access to DICOM persistent Objects (WADO) protocol, or images can be browsed or accessed via a local URL.
Once again, this is a view-only system, so there’s no editing. The link above will take you to the full wiki, and demos can be found here. While the GitHub version requires some programming knowledge to implement, you can also get DWV as a Chrome extension, a Google Drive app, or a WordPress plugin. Visit the GitHub link for more information.
Mango
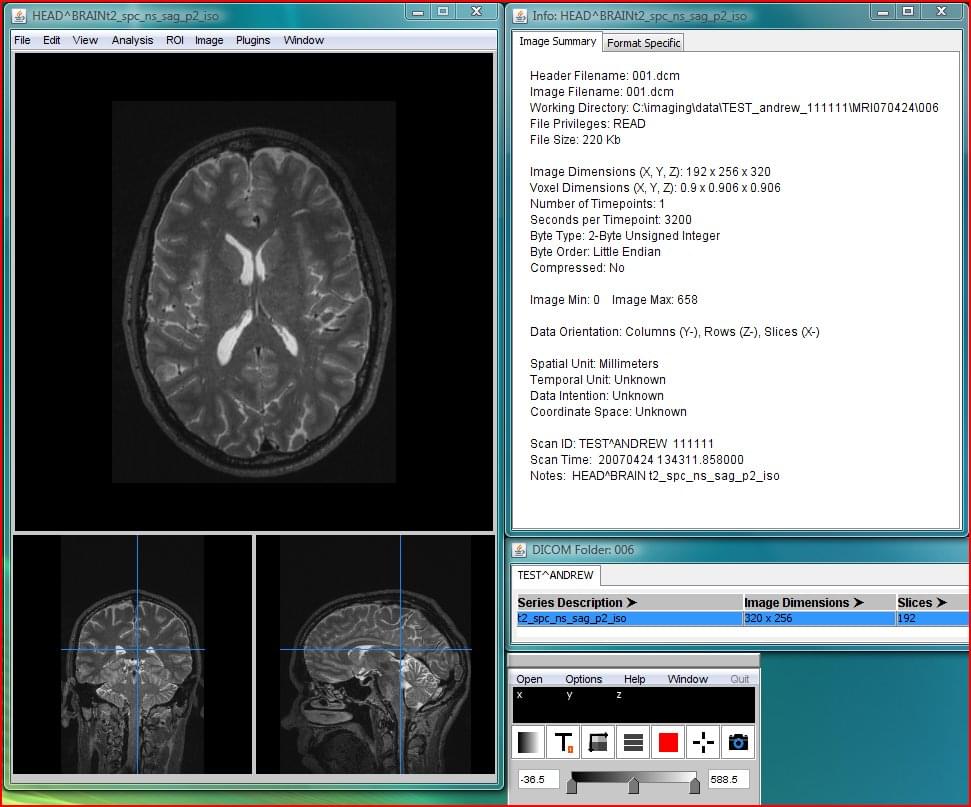
One of the most advanced systems on our list, Mango — or Multi-image Analysis GUI — is available in three versions, for Windows, Macintosh, or Linux <desktops (Mango), browser (Papaya), or iPad (iMango). The browser version does require some coding, so you’ll need some knowledge of HTML and JavaScript to use it. Developed by Jack Lancaster, Ph.D. and Michael Martinez at the University of Texas Health Science Center’s Research Imaging Institute, Mango supports DICOM, NEMA-DES, MINC, and NIFTI image formats, VTK, GIFTI, and BrainVisa surface rendering formats. It even can create custom imaging formats and filters.
Mango offers a host of analysis, processing, and editing features, and can convert, anonymize, and register images. It offers more functionality than many commercial systems, thanks to initial and ongoing support via grants from the National Institute of Mental Health and the National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering.
Escape EMV
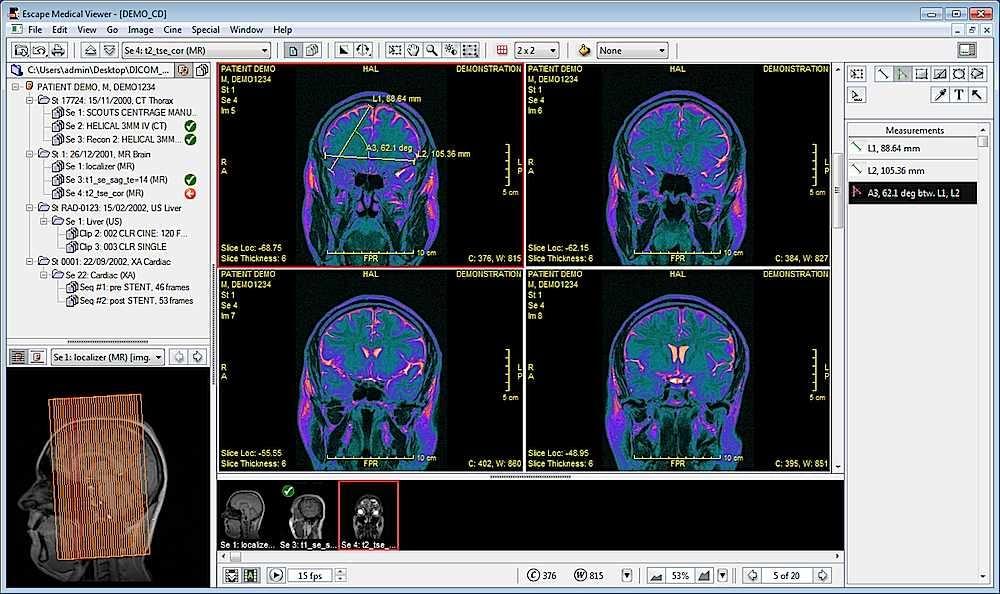
EMV is a lightweight DICOM viewer that can open most DICOM images and DICOMDIR files from CD/DVD, flash drives, etc. The software comes in two different versions, a recently updated version for Mac, and an unsupported version for Windows. EMV can access WADO PACS systems to retrieve studies. It can handle user objects, like annotations and measurements, and is available in English, French, Italian, Spanish, and Portuguese versions.
The tool offers anonymizing capabilities, can export images, and the viewer offers various displays, overlays, filters, marking, and colorizations. It requires QuickTime to work, which is why the Windows version is unsupported. While you can download and demo the software for free, using it in a commercial environment requires a €245 license for up to three computers.
IrfanView
Yes, that IrfanView, the simple free image viewer you may have downloaded in the early 90s to view .gifs, .tiffs, and other image files now supports DICOM viewing. It is provided as freeware for non-commercial use, so if you want to use it in your medical practice you’ll need to register it and pay a one time, $12 licensing fee, but if all you want is a lightweight program to view simple DICOM images on your Windows desktop, IrfanView is hard to beat.
***
This is not intended to be a comprehensive list — there are hundreds, if not thousands of software solutions for viewing, editing, and otherwise manipulating DICOM and other medical imaging formats. An ideal DICOM viewing platform would involve access to an in-house or networked PACS server at the radiology center of your choosing, but we recognize that many physicians are not operating under ideal circumstances.
Having trouble deciding which EHR system is the right solution for your business? Check out our EHR EMR Software Product Selection Tool to find the best fit or contact us to speak with one of our Tech Advisors. They will be happy to help. Best of all? It’s free.
Top Electronic Health Record Software Recommendations
1 Domo
Build a modern business, driven by data. Connect to any data source to bring your data together into one unified view, then make analytics available to drive insight-based actions—all while maintaining security and control. Domo serves enterprise customers in all industries looking to manage their entire organization from a single platform.
Need a Little Help?
Talk with a software expert for free. Get a list of software that’s great for you in less than 15 minutes.
2 Kareo
Kareo offers medical practices a cloud-based electronic health record solution paired with award-winning practice and revenue cycle management. Kareo EHR is designed for use by physicians in an outpatient setting and is qualified to help medical practices earn Meaningful Use attestation. The appeal lies in its affordability, usefulness, and mobile capabilities. Kareo EHR includes dynamic patient, document, and medication management functions.